Certificate requirements
You need to have a PKI in your environment with at least one Issuing CA. Each server that has 1E Server components installed requires its own Web Server certificate (except for a remote SQL Server). By default, every client requires a client authentication certificate.
Client-Switch communication uses WebSocket Secure protocol, whereby each client establishes a secure link to the Switch, which is then used by the Switch to send instructions to the client. This is shown as a dotted line in the pictures on the Communication Ports page.
All other communications from external devices use HTTPS, including client connecting to the Background Channel in order to download resources that may be required by instructions, and using the 1E Portal to administer and use the system.
All communication is encrypted, which requires a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
PKI certificates
PKI is required for:
Web Server certificate - prerequisite for each 1E server website, must contain all the DNS Names used for the server
1E server's client authentication certificate - only on 1E servers hosting a Background Channel, and only if using Content Distribution
Client authentication certificates - each 1E Client uses the device's client certificate to authenticate itself to 1E Switches
Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) - 1E Clients and Switches use HTTP-based CRL Distribution Points to validate certificates
Code signing certificates - used for signing custom and modified instructions, so they can be imported into 1E and then run
Digital signing certificates - used for signing 1E software.
Request-signing certificates
Your 1E system requires these certificates for signing requests between internal and external components, including your Identity Provider (IdP). This is a requirement since 8.1.
Signing certificate for platform tokens is used to sign requests between 1E platform components. All 1E servers must share the same certificate. This means the certificate needs to be created with its private key exportable, and then imported on each server.
Signing certificate for IdP requests is used by the platform server to sign authentication requests to your IdP, and Directory Searches. The public key of this certificate must be exported (for example as a Base-64 encoded X.509 CER file, without private key) and uploaded to the IdP client assertion application you have configured for Directory Searches.
Signing certificate for integration tokens is only required if you are using any integration features that use non-interactive logins, such as a ServiceNow integration apps, 1E Authentication Proxy, unattended scripts, integration by Shopping, or NightWatchman Enterprise. The public key of the certificate must be exported (for example as a Base-64 encoded X.509 CER file, without private key) and uploaded to the IdP client assertion application you have configured for non-interactive logins. You may decide that each integration feature has its own certificate. You can also decide that each feature has its own client assertion application for non-interactive logins, each with its own certificate.
These certificates can be issued by a PKI but do not have to be, they can be self-signed. Unless specified above, they have no specific requirements other than they must be CNG. Unlike certificates used for web servers, where there is a requirement that there be a trust chain to a root CA certificate, these certificates can be self-signed. This is because the trust relationship is defined either between platform components, or between a platform service and the identity provider, or between integration features and the identity provider. Both parties in each relationship has local access to their certificate and can thus prove their identities using standard cryptography sign/verify procedures.
Warning
Each platform IdP certificate must be created specifically for its own purpose. Do not use the same certificate for Signing certificate for platform tokens Signing certificate for IdP requests, and Signing certificate for integration tokens, and do not use the Web Server certificate.
Creating the certificates
Before installation of a 1E server, you need to have installed certificates in the server's local machine certificate store. You can use the PowerShell cmdlet new-selfsignedcertificate to create self-signed CNG certificates in the local machine certificate store. Although these certificates have no specific requirements other than being CNG, you can apply other certificate attributes, such as the subject, to reflect your corporate policies. For information about this cmdlet, refer to learn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/pki/new-selfsignedcertificate.
The following PowerShell command creates a self-signed CNG certificate in the local machine certificate store, with your specified subject, RSA (2048) encryption, and default expiry of 1 year, the private key is exportable.
new-selfsignedcertificate -subject CN=<subject>
Note
Refer to AAD Applications for details about the self-signed certificate requirements Azure AD apps need for 1E 9.0, this guidance includes how to create and configure these apps.
Important
1E recommends you do not run this command directly on a 1E server because it is more secure that each of these certificates is stored with its private key not exportable.
Therefore, the above command should be run on a different computer. The certificate is then exported as a PFX file (with a password) before deleting it from the certificate store. The PFX file can then be re-imported onto relevant servers, without marking the private key as exportable.
This PFX process is anyway necessary if you have multiple servers sharing the same Signing certificate for platform tokens certificate.
The public key of the Signing certificate for IdP requests certificate must be uploaded to the IdP application you have configured for Directory Searches
The public key of the Signing certificate for integration tokens certificate(s) must be uploaded to the corresponding IdP application(s) you have configured for Non-interactive logins
The public key of a certificate can be exported for example, as a Base-64 encoded X.509 CER file, without private key
The Network Service account on each 1E server requires read access permission on each certificate. Permission can be granted manually before, or automatically during installation by using the Add permissions for the private key link in the 1E Server Setup wizard.
Tip
What are CNG certificates?
CNG is the "next generation" of CryptoAPI (CAPI) service providers, that has actually been available for many years.
If you did not use the above method of creating your certificates, you may need to check they are CNG. To check if a certificate is CNG, look to see if its ProviderType and KeySpec values are both 0.
You can check this using the Windows certutil utility, and one of the following commands to make a verbose dump of certificate(s).
certutil -v -store my certutil -v <path to PFX file>
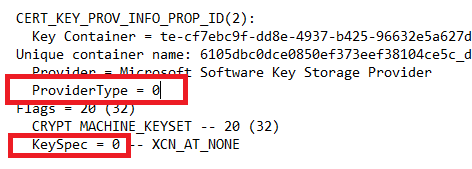
Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider is one of several CNG providers. Run certutil -csplist to see a list of crypto service providers on your Windows computer.
Public Key Infrastructure
You need to have a PKI in your environment with at least one Issuing CA.
1E requires each Issuing CA has:
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Distribution Point (CDP) that uses HTTP/S.
This HTTP/S CDP information included in certificates issued to 1E Server and client devices.
PKI notes
If you have an existing PKI and have just added a new CDP to support HTTP/S then you will need to re-issue certificates to your servers and devices.
1E web server deliberately does not work with self-signed certificates for security reasons. Therefore, 1Eservers cannot be installed on the same server as a Root CA, because its certificate is self-signed. For the same reason, 1E Client cannot be installed on a DC unless the client's Switch is configured to not require client certificates.
1E supports TLSv1.2 and TLSv1.3. If your PKI is using SHA512, then please ensure that your environment has relevant updates applied, as described in KB2973337. See Enabling SHA-512 to work with TLSv1.2.
If you want 1E to manage legacy OSs that Microsoft no longer supports, there may be issues with encrypted certificates described in Constraints of Legacy OS.
Note
1E Client and 1E Switches use OpenSSL and its validation process to verify certificates. Websites use Microsoft IIS validation methods.
Web Server certificate
Each server that has 1E server components installed requires its own Web Server certificate (except for a remote SQL Server). This certificate is also used by the Switch and the Coordinator. Therefore, a single-server installation requires only one Web Server certificate. This certificate must be provided on the server prior to installation of 1E.
The Web Server certificate requires the minimum of the following:
Issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA)
The certificate for the Root CA in the Certification Path must exist in the Trusted Root CA store of the server
If the issuing CA is not the Root CA then the certificate for the issuing CA and any intermediate CA in the Certification Path must exist in the Intermediate CA store of the server
The above CA certificates must exist on the 1E Web Server and Windows client devices
Most organizations have automated distribution of these CA certificates to servers and clients, using Group Policy for example.
Has at least the following Key Usage:
Digital signature
Key encipherment.
Has at least the following Enhanced Key Usages:
Server Authentication.
Revocation information is included
References at least one CRL Distribution point that uses HTTP - see DMZ Server note below.
Must have a private key available.
Tip
The default template Web Server available with a Microsoft PKI is suitable for requesting a 1E Web Server certificate.
DMZ Server
Please ensure you note the additional certificate requirements described below, when installing any server in a system that also contains a DMZ Server. Internal Master and Response Stack servers, and DMZ Server, each require two HTTPS bindings, as described in DNS Names. For even more detail, please refer Implementing a 1E DMZ Server.
Also note the requirement for server certificates to reference at least one CRL Distribution point that uses HTTP. These CRL DPs are likely to be in the internal network, and the firewall will need to allow the DMZ server to access these internal servers.
Web Server certificates used by a 1E servers must be issued with their fields set as follows. Example DNS Names are discussed in DNS Names.
Fields | Example Option 3 type certificate | |
|---|---|---|
Subject Common Name Field (subject:commonName) | Subject (CN) can be any valid name, and is no longer mandatory as required by previous versions of 1E. | |
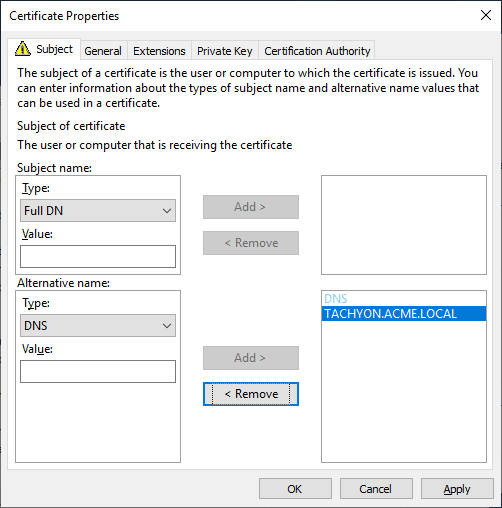
Subject Alternative Name Extension (extensions:subjectAltName), type dnsName | The 1E server DNS Name FQDN (DNS Alias) of the server. This is mandatory, same as required by previous versions of 1E. On a Master Stack - example: DNS Name=TACHYON.ACME.LOCAL On a Response Stack - example: DNS Name=TACHYONRS.ACME.LOCAL On a DMZ Server - example: DNS Name=TACHYONEXT.ACME.COM | |
Subject Alternative Name Extension (extensions:subjectAltName), type dnsName | An Alternate DNS Name FQDN (DNS Alias) of the server. This is usually mandatory, for example if there is more than one server in your 1E system, as discussed in DNS Names. On a Master Stack, example: DNS Name=TACHYONALT.ACME.LOCALorDNS Name=TACHYON.ACME.LOCAL On a Response Stack - example: DNS Name=TACHYONALT.ACME.LOCAL On a DMZ Server - example: DNS Name=TACHYONDMZ.ACME.LOCAL | |
Example |
|
Note
Earlier versions of 1E required the certificate to have a CN and used SAN fields differently. If you are upgrading your 1E server from an earlier version, it may still be using this type of certificate. When upgrading 1E, you can issue a replacement certificate, or continue using the old style certificate (because the new-style certificate requires only a SAN DNS Name that matches the DNS Alias, which are provided by the old style certificates).
Examples of old-style certificates:
Fields | Example old Option 2 type certificate |
|---|---|
Subject Common Name Field (subject:commonName) | The computername FQDN of the server Example: CN=ACME-TCN01.ACME.LOCAL |
Subject Alternative Name Extension (extensions:subjectAltName), type dnsName | The DNS Alias FQDN of the server Example: DNS Name=TACHYON.ACME.LOCAL TipAdd any additional DNS Names here. |
Example certificate request | 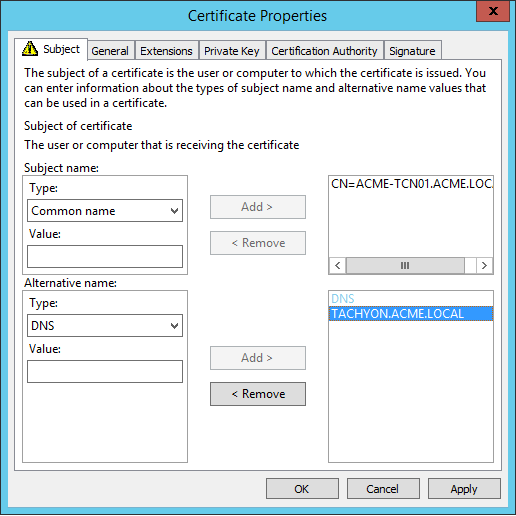  NoteOption 2 type certificates required the CN to be the computername FQDN, and the list of Subject Alternate Names (SAN) to contain the DNS Alias. Also, prior to 1E 5.0 the certificate required its private key to be exportable. 1E 5.0 and later is able to use this type of certificate when upgrading from an earlier version of 1E. |
Fields | Example of old Option 1 type certificate |
|---|---|
Subject Common Name Field (subject:commonName) | The DNS Alias FQDN of the server Example: CN=TACHYON.ACME.LOCAL |
Subject Alternative Name Extension (extensions:subjectAltName), type dnsName | The DNS Alias FQDN of the server Example: DNS Name=TACHYON.ACME.LOCAL The computername FQDN of the server Example: DNS Name=ACME-TCN01.ACME.LOCAL |
Example certificate request | 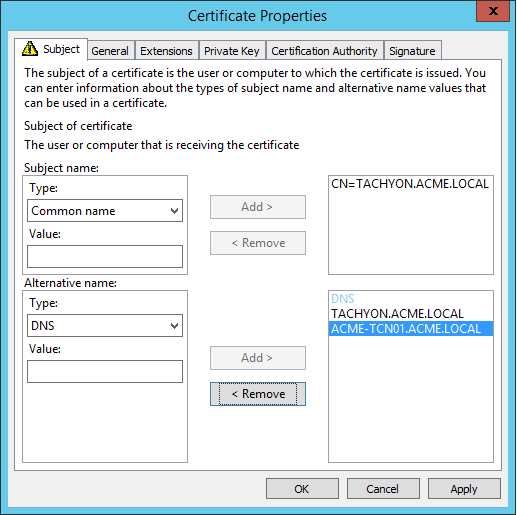  NoteOption 1 type certificates required the CN to be the DNS Alias, and the list of Subject Alternate Names (SAN) to contain the computername FQDN. Also, prior to 1E 5.0 the certificate required its private key to be exportable. 1E 5.0 and later is able to use this type of certificate when upgrading from an earlier version of 1E. |
The following need to be considered when requesting this type of certificate.
The certificate can be used only on the server it was intended, that has the correct computername FQDN and DNS Alias FQDN.
It is not possible to use the Create Certificate Request method in IIS Manager Server Certificates, because it does not support all the above requirements.
If you have a Microsoft CA, and a suitable Web Server template has been issued and enabled in the Directory Enrollment Policy, then it is possible to Request New Certificate in the Certificates (Local Computer) mmc snap-in and use the Certificate Enrollment wizard.
Many organizations have their own process for submitting a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Please ensure all the above requirements are specified. Security administrators sometimes have difficulty providing a certificate with one or more Subject Alternative Names (SAN), and it helps to explain these are type DNS.
If you have a Microsoft CA then it is simplest to use the Certificate Enrollment wizard available in the mmc certificates snap-in, to request a Web Server certificate and fill in the details.
1E server's client authentication certificate
When Content Distribution is installed, any server hosting a Background Channel must have a Client Authentication certificate. This can be the same certificate as a Client authentication certificates if you have 1E Client installed, or it can be the same certificate as the Web Server certificate if your organization security policy allows your Web Server certificates to be used for both Server Authentication and Client Authentication.
The Background Channel proxy uses this certificate to be authenticated by the Content Distribution Web API, and must be available on the server so that it can be selected on the 1E Server Setup Content Distribution screen during installation.
Client authentication certificates
Note
You can use 1E Server Setup to install 1E so it does not require 1E Clients to present certificates to the 1E Switch. 1E can be reconfigured later to re-enable use of client certificates when your environment is ready. Each 1E server requires a Web Server certificate. Please contact your 1E Account Team if you need help with this.
Note
The 1E Client requires that the client certificate it presents to the platform has both the Signature and Encryption request handling options. These options are the defaults if provisioning using a Computer Certificate template from a Microsoft Windows Certificate Authority. If you are using a custom template, or an alternative certificate authority, you should confirm that both these options are enabled.
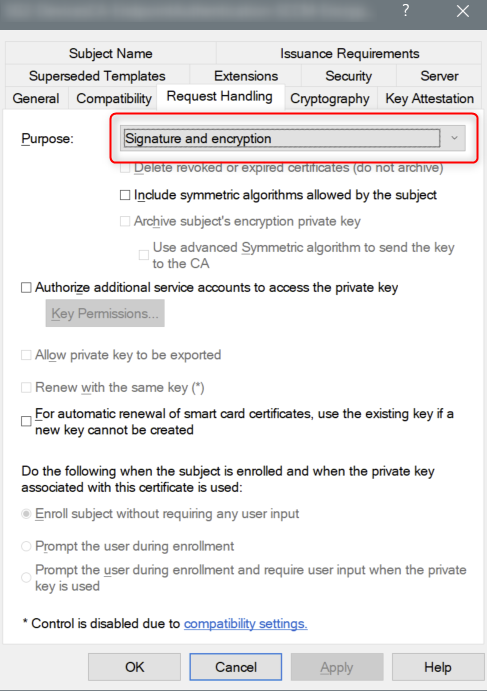
If you have configured 1E to require client certificates (Client certificates) then each device requires a certificate with the following properties, so the 1E Client can be authenticated by the 1E Switch.
Issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA):
The certificate for the Root CA in the Certification Path must exist in the Trusted Root CA store of the client.
If the issuing CA is not the Root CA then the certificate for the issuing CA and any intermediate CA in the Certification Path must exist in the Intermediate CA store of the client.
If either of these CA certificates are different to those used by the 1E Web Server, they will need to be exported and imported on the 1ETachyon Web Server.
Most organizations have automated distribution of these CA certificates to clients and servers, using Group Policy for example.
Has at least the following Enhanced Key Usage:
Client Authentication.
Has at least the following Key Usage:
Digital Signature.
Key encipherment.
Has a private key:
For workgroup and non-Windows devices, the private key must be exportable.
Revocation information is included:
References at least one CRL Distribution point that uses HTTP.
Has a Subject Name of type Common Name (CN=<computername>) or Subject Alternative Name (DNS Name=<computername>) where <computername> depends on the type of device:
On domain-joined Windows PCs this must be the computername FQDN of the computer, for example W701.ACME.LOCAL.
On workgroup Windows PCs and non-Windows devices, this must be the computername of the computer - as returned by the hostname command, for example on Windows PC this could be W701, and on a Mac this could be MAC01.local.
Note
1E clients and Switches use OpenSSL and its validation process to verify certificates.
The client device's certificate is stored differently depending on the type of OS:
For Windows devices, the certificate is stored in the Windows Local Computer personal certificates store.
For non-Windows devices, except for the Mac, the Tachyon client does not use proprietary certificate stores. Instead, the client requires the certificate exists as a .pfx file in the client installation folder structure. For more information, please refer to Client certificates.
For macOS, you have a choice of storing the client certificate in the macOS Key Store or using the .pfx file approach required by other non-Windows devices. Please refer to Client certificates.
If using a Microsoft Enterprise CA then the following should be considered.
For domain joined Windows computers:
Use the Computer template or a duplicate.
Enable auto-enrollment - so that devices enroll automatically.
For workgroup Windows and non-Windows devices:
Use a duplicate or equivalent of the Computer or Workstation template.
The template's Subject Name uses supply in the request - so the hostname can be entered when requesting a certificate.
The template must Allow private key to be exported - so a certificate can be requested on a domain joined Windows computer, exported as a .pfx file and then imported on the target device (see non-Windows Device Certificate).
If using a standalone CA, then certificates must be deployed by other means.
Code signing certificates
You will need your own code signing certificate, and have it registered in your 1E license, if you want to develop your own custom 1E instructions, or modify those of other authors. Instructions that are provided in the 1E platform zip or downloaded from the 1E Exchange have already been code signed using the Platform and 1E Exchange certificates from 1E. Your 1E license controls whether you can use these instructions.
Ideally, all of your 1E instruction developers should share a single code signing certificate between them. Each code signing certificate must be registered in your 1E license and associated with your organization's instruction name prefix. When you have chosen your prefix and have your code signing certificate(s) you then need to send details of these to 1E, who will update your 1E license. This will then automatically activate on your 1E server (assuming it has connection to the Internet).
The following applies to the importing and running of custom 1E instructions:
1E platform will only allow instructions to be imported if they have been signed and the code-signing certificate exists in the 1E server's Trusted Publishers certificate store.
For SaaS customers you will need to supply the certificate public key to 1E, and will need the prefix and thumbprint added to your license, contact your 1E account representative for details.
1E platform will only allow instructions to be run if their prefix and code-signing certificate have been registered in the 1E server's license file (even if the instruction has been successfully imported, it will be flagged as unlicensed if the license information is not there).
Custom Instructions must be signed by TIMS using a code-signing certificate present in the Personal certificate store where TIMS is installed (either local user or machine store). The TIMS user signing the Instruction also needs to have access to the certificate's private key.
For a getting started guide to configuring and verifying your 1E system so that you can run customized 1E instructions, refer to Running instructions for the first time.
Digital signing certificates
On Windows computers, the installation MSI files, and binary executable and DLL files of 1E software are digitally signed. The 1E code signing certificate uses a timestamping certificate as its countersignature. 1E occasionally changes its code signing certificate, as shown in the table below, and uses it for new releases and hotfixes for older versions, as shown in the table below.
The signature algorithm of the 1E code signing certificate is SHA256RSA. In most cases, the file digest algorithm of an authenticode signature is SHA256, and the countersignature is a RFC3161 compliant timestamp. The exception is on legacy OS (Windows XP, Vista, Server 2003 and Server 2008) which require the file digest algorithm of an authenticode signature to be SHA1, and a legacy countersignature.
The root CA certificates (for signing and countersigning) must exist in the Third-Party Root Certification Authorities store (which is replicated in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store). These root CA certificates are normally automatically provided by Microsoft's Update Root Certificates feature, however, this may not be true for legacy OS computers in a lab environment that are not connected to the Internet.
The table below applies to software and hotfixes released in 2020.
2020 | Signing certificate | Timestamping certificates |
|---|---|---|
Certificate | 1E Limited | TIMESTAMP-SHA256-2019-10-15 and DigiCert Timestamp Responder |
Issuing CA | DigiCert EV Code Signing CA (SHA2) Thumbprint: 60ee3fc53d4bdfd1697ae5beae1cab1c0f3ad4e3 | DigiCert SHA2 Assured ID Timestamping CA Thumbprint: 3ba63a6e4841355772debef9cdcf4d5af353a297 and DigiCert Assured ID CA-1 Thumbprint: 19a09b5a36f4dd99727df783c17a51231a56c117 |
Root CA | DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA Thumbprint: 5fb7ee0633e259dbad0c4c9ae6d38f1a61c7dc25 | DigiCert Assured ID Root CA Thumbprint: 0563b8630d62d75abbc8ab1e4bdfb5a899b24d43 |
PKI in the cloud
1E relies on both client (device) and server side certificates to ensure secure communication. In order for these certificates to work the computers need to trust the PKI implementation (issuing Certification Authority and chain of trust). In a standard on-premises environment, devices can be enrolled with certificates using Directory Group Policy.
It is possible to use a non-Windows based PKI, but it is then left as an exercise for the user as to how to distribute and enrol device certificates to all end-points.
Given the supported Directory configuration above, the PKI requirements described above still apply to a cloud based implementation.
1E Web Server certificate
Since clients must be able to access the 1E Switch and Background Channel from both the internal corporate network and the Internet, there are some additional considerations when creating the 1E web server certificate.
The server must have a consistent external FQDN.
In AWS, a standard EC2 instance has an external FQDN based upon its externally accessible IP address. However, this IP address will change each time the server restarts, and since the 1E Switch relies on an HTTPS certificate that utilizes the FQDN to authenticate the server, this would cause the Switch to stop working. In order to work around this, any AWS implementation MUST use an Elastic IP address associated with the network interface of the Switch to ensure that the IP address never changes, and therefore the external FQDN is always the same. Alternatively, you can create a CNAME entry in your external DNS to point to the external FQDN of the AWS instance and use the CNAME as the subject name of the server certificate.
The web server certificate must incorporate all DNS Names that will be used to access the server in the certificate SAN.
Clients can be configured to connect to multiple Switches for resilience and geographic load balancing. In many cases a cloud based virtual machine may be able to be accessed through both an internal VPN network, and an external Internet connection. These connections can be made using the same DNS name (via a CNAME entry as specified in the main documentation) or by different DNS names (where there are separate internal and external DNS domains in use).
The certificate crafted for the 1E Switch must contain all DNS Names that will be used to contact the server in the Subject Alternate Name (SAN) entry within the certificate.
Client certificates
Any devices that will connect to the 1E implementation must have a client certificate from a PKI infrastructure trusted by the 1E server. In a Windows domain environment, this is usually provided through an Enterprise Certificate Authority and the use of Group Policy. It is also possible to provide certificates through SCEP, which 1E has tested and support the use of the Microsoft Device Enrollment Service (MDES) for this purpose. Use of other SCEP solutions will be supported on a best-efforts basis.