Network requirements
The correct choice of DNS Names for your 1E Servers is perhaps the most fundamental decision you will make.
You must ensure the firewalls on your client, servers, and network are configured correctly, and your Internet connections to the 1E Cloud are whitelisted.
For a remote SQL Server, please refer to Configuring a persistent route for SQL traffic. However, please ensure you also consult your server, firewall and networking teams.
Firewall Ports
The following are extracts from the Communication Ports reference page.
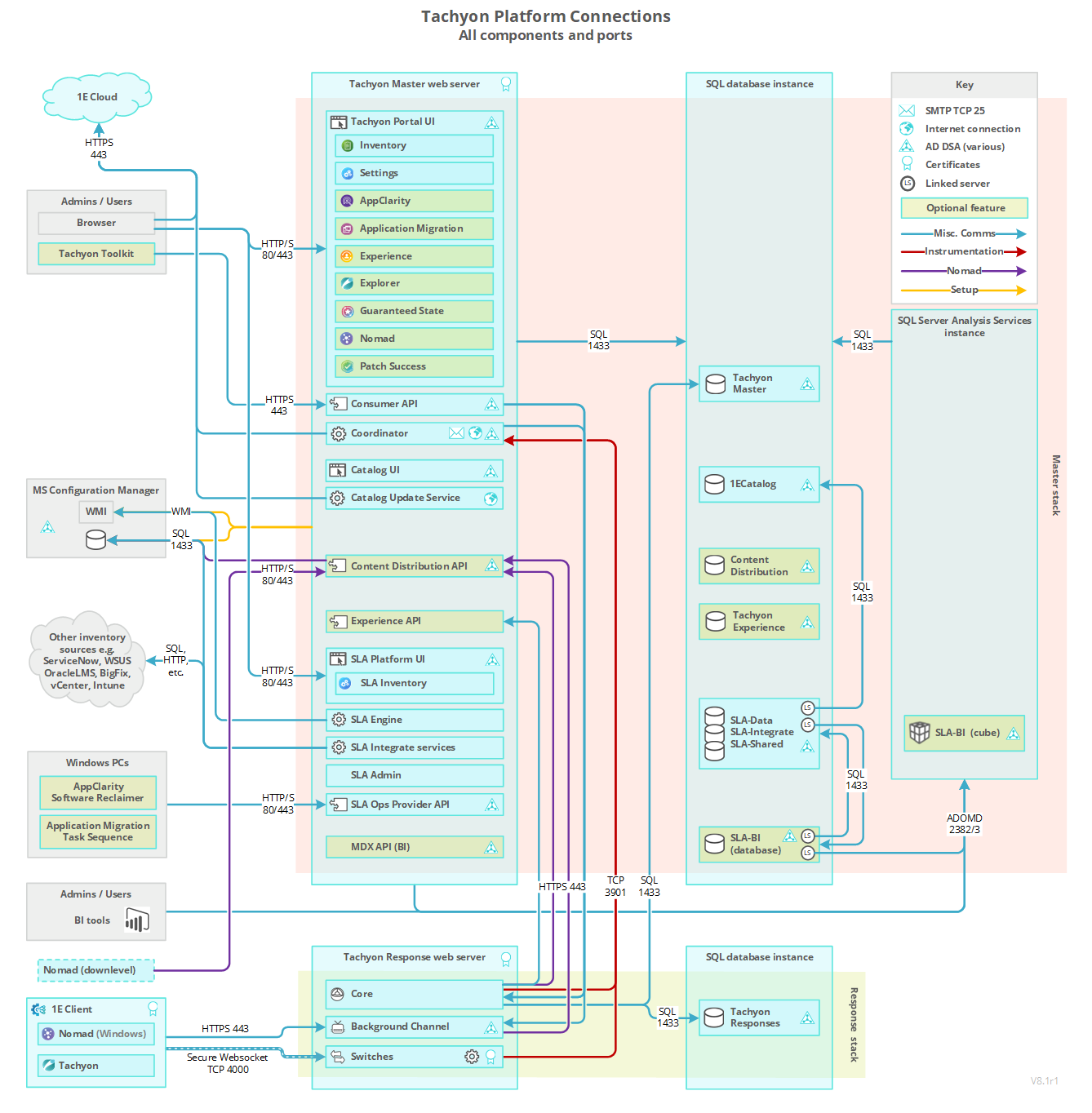
The following table lists firewall requirements for a single-server where 1E Master Stack and Response Stack are installed on the same server. The table assumes a remote SQL Server hosting TachyonMaster and TachyonResponses databases. Each 1E component described in the table has at least one output and/or input. For each 1E component with an output, there is a matching input.
Firewalls normally protect against incoming traffic from remote devices, however, the table below also includes outgoing connections. The table does not include internal communications within the Server.
In addition to but not included in the table are various ports that 1E uses to communicate with Microsoft services, including Certificate Services and Active Directory. The Coordinator Workflow service queries AD for email details; the Consumer API queries AD for security details.
Port requirements are not provided here for the Content Distribution, Shopping, and WakeUp modules of the 1E Client. Only the ports used by the 1E Client feature of the 1E Client are listed.
If the 1E Nomad module is being used by the 1E Client on Windows computers, it has additional port requirements of its own, which are not changed by 1E.
Additional ports may be required if 1E instructions need to connect to non-1E content sources.
Additional requirements may exist if the environment has changed default security settings.
1E Servers
Device | Port | Protocol | Direction | Usage | Configurable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 443 | HTTPS | Incoming |
| Yes, during installation. In the Website Configuration panel in 1E Server Setup. See HTTPSIISPORT. Setup installs other components using the same settings as 1E Server. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 80 | HTTP | Incoming |
| Yes, during installation. In the Website Configuration panel in 1E Server Setup. See HTTPSIISPORT. Tachyon Setup installs other components using the same settings as Tachyon Server. |
1E Server (Response Stack) | TCP 443 | HTTPS | Incoming |
| Yes, during installation. In the Website Configuration panel in 1E Server Setup. See HTTPSIISPORT. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 443 | HTTPS | Outgoing |
| The port used to connect to the 1E Cloud Services is not configurable. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 6002 | WebSocket (ws) | Incoming Outgoing |
| Yes, configurable after installation. NoteIntegrate Agent component is not shown on the diagram, and installation on remote systems is not supported. |
1E Server (Response Stack) | TCP 4000 | WebSocketSecure (wss) | Incoming |
| Switch ports are not configurable using the Server installer. A Switch port can be changed post-installation, by configuring the value in the Port column for the relevant Switch in the SwitchConfiguration table in the 1E Master database. If the Switch port is changed after deploying 1E Client (with 1E features enabled) then the corresponding Switch port must be updated in each Client's configuration file. Clients initiate and maintain a WebSocket Secure connection to a Switch, which the Switch uses to communicate back to the clients. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 25 | SMTP | Outgoing |
| Yes. In this version of 1E, SMTP Authentication is not configurable using the Server installer. The default is anonymous authentication. However, it can be changed post-installation. For details of changing the SMTP configuration and disabling email notifications, please refer to Changing the SMTP Host configuration. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 1433 | TDS | Outgoing |
| Not configurable from Setup. In the Database Servers panel in 1E Server Setup you can select a SQL Server instance. The instance can be installed using a non-standard port. However, selecting an instance that uses a non-standard port will not change the port used by the 1E Installer, and installation will fail. If you require the use of a non-standard port on a Default SQL Server instance, contact 1E for guidance on a manual workaround. If using a Named Instance that is set to its default configuration where the server automatically chooses a random port (or if you manually configured the instance to use a fixed port), then the SQL Browser service needs to be enabled to let the 1E Server determine the port in use. You will need to open UDP port 1434 used by the SQL Browser. See SQLSERVER_MASTER. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 1433 | TDS | Outgoing |
| Configurable in various Connectors, please refer to Connectors page. |
1E Server (Master Stack) | TCP 135 and 445 (initially) | WMI (DCOM) | Outgoing |
| Not configurable. Please refer to Provider configuration page and Content Distribution. |
1E Server (Response Stack) | TCP 1433 | TDS | Outgoing |
| Not configurable from Setup. See the comments above for the 1E Server (Master Stack). See SQLSERVER_RESPONSES. |
SQL Server (TachyonMaster database) | TCP 1433 | TDS | Incoming |
| Not configurable from Setup. See the comments above for the 1E Server (Master Stack). See SQLSERVER_MASTER. |
SQL Server (TachyonResponses database) | TCP 1433 | TDS | Incoming |
| Not configurable from Setup. See the comments above for the 1E Server (Master Stack). See SQLSERVER_RESPONSES. |
Whitelisting connections to 1E Cloud
The simplest method is to whitelist *.1e.com
The following sections briefly describe 1E features which connect to the 1E Cloud.
For guidance on whitelisting and configuring Internet Explorer proxy settings, please refer to Preparation.
1E license service URL
Ensure the following URL is whitelisted:
This URL must be accessible from the 1E server during setup and running of 1E.
The 1E license must be validated on a regular basis via internet contact with the 1E license service. The regular validation period is set when the license is requested.
For whitelisting purposes, the 1E server (specifically the Coordinator Workflow module in the Master Stack) requires an Internet connection to the 1E license service, as defined in the license file itself. If activation fails, then the system will install but not be usable until activation is completed.
Upgrading
When upgrading, you are recommended to get a new license file and update your whitelist with the new URL. The old URL (https://license.1e.com) is suitable only for 8.0 and earlier. However, if you are upgrading and your license file has the old URL then you should also whitelist the old URL.
1E setup will report a warning in the 1E Server Setup screen if it is unable to connect to the 1E license service. This is important only on the 1E Master Stack Server, not on other types of 1E server. You can test the connection using 1E setup or using Internet Explorer.
Tip
If you are whitelisting an IP address and your server has multiple network interfaces, then you can configure a persistent route using a similar process described in Configuring a persistent route for SQL traffic.
Your 1E server may not be able to connect to the 1E license service if your environment is using web proxy servers. Contact your 1E Account Team for advice in case you have this type of setup.
1E Catalog service URL
Ensure the following URL is whitelisted:
https://catalog.1e.com
This URL must be accessible from the 1E Server during setup and running of 1E Catalog. This enables the Catalog Update service to connect to the 1E Cloud Catalog and download the latest catalog entries.
Note
1E Catalog may need additional configuration to support proxy servers, but this depends on the configuration you have in your current environment. Please contact 1E Support if you need help doing this.
1E Analytics URL
Ensure the following URL are whitelisted for clients and 1E servers:
https://analytics.1e.com
https://data.analytics.1e.com
https://content.analytics.1e.com
https://_460897a4cf2c02443c6af6aed8761f7b.content.analytics.1e.com
Or simply *.analytics.1e.com or *.1e.com
User Interface telemetry reports how the user interface is used, and data is sent directly from administrator browsers to the 1E Cloud.
Telemetry features are configurable using 1E Server Setup during installation or upgrade, and can be enabled or disabled as a post-installation task. 1E encourages customers to enable sending telemetry.
For more information, please refer to Telemetry.
Network interfaces
The following conditions apply to network interfaces, which must be configured before installing 1E on a server. Each network interface must be assigned a static IP Address.
Switches | Each Switch supports up to 50,000 devices and requires its own network interface, with a minimum speed of 1Gbps. Switch interfaces can be on the same or different subnets. Each interface can have its own DNS Name or share the same DNS Name as explained in DNS Names below. If necessary, these interfaces can be shared with a Background Channel or other 1E services, which may share the same DNS Name or have their own names. |
Response Stack with a Core component using a remote SQL Server instance and more than 500 devices | In addition to the Switch interfaces, another interface is required for outgoing response traffic from the Response Stack Core to its remote SQL Server. This should have a minimum speed of 1Gbps, or 10Gbps if the Response Stack has 3 or more Switches. This is required to ensure optimum performance when SQL Server is remote. Network routing on the Response Stack server must be configured so that SQL traffic is routed over this interface. The simplest method is to route all outgoing traffic. The interface used for SQL traffic should not register its IP Address in DNS to avoid unnecessary incoming traffic and accidentally becoming part of a round-robin DNS Name used for Switches. |
DMZ Server | An additional internal facing interface is required for outgoing response traffic from Switches on the DMZ Server to the Core on the internal 1E Response Stack. This should have a minimum speed of 1Gbps. As stated above, each Switch must have it own external facing interface, used for incoming response traffic from clients to Switches. The external facing interface(s) can also be used for clients to the Background Channel. The simplest way to ensure the internal interface is used for outgoing traffic is for it to be on a different subnet to the external interface(s) with no routing between them - this is normal in a DMZ. |
Administration traffic for a 1E Master Stack does not have any additional network requirements.
Tip
1E Server Setup supports installation using IPv4. If you have a working IPv6 environment, then please contact 1E for advice on using that.
For the remote SQL Server requirement, please refer to Configuring a persistent route for SQL traffic. However, please ensure you also consult your server, firewall and networking teams.
Network impact
Most of the network traffic experienced by a 1E system is compressed responses from clients to Switches. Responses to 1E instructions are returned by online clients in a matter of a few seconds. 1E is designed for speed without impacting your network.
The Response Stack's Core then processes and stores uncompressed responses in the 1E Responses database. If the database is remote then this will create significant network traffic when saving responses, but normally this will be within a datacenter. Even so, a dedicated interface is recommended on each Response Stack for connection to a remote SQL Server in order to prevent network contention between incoming and outgoing response traffic.
Other network traffic generated by 1E is low by comparison. Endpoint Troubleshooting is a single page application which uses paging to view responses.
1E clients also download content from a Background Channel, which is a website hosted on the same server as Switches. They deliberately stagger the delay of their download for up to 5 minutes (configurable). By using Content Distribution, you can avoid the staggered delay on Windows PCs without impacting your network. For further information about Content Distribution please refer to Downloading client content and Content Distribution integration below.
WAN caching
Communications between 1E platform clients and Switches should not be cached or delayed, which can be prevented by excluding the Switch port(s) or the IP Addresses of Switch interfaces on caching devices.
Communications between clients and the Background Channel can be cached, however, please refer to Downloading client content and Content Distribution integration as an alternative to WAN caching.
Isolated Networks
1E can operate in a multi-domain, multi-forest environment with client devices on internal and external networks, supporting internal and external Certificate Authorities.
Each client device must have a network connection to a Switch and Background Channel, with the necessary network firewall ports open. If clients are unable to connect to the 1E server on the corporate network, then it is necessary to install additional 1E servers.
DNS Names
Each server that has 1E platform components installed requires its own DNS Name. A DNS Name can be a DNS alias, CNAME or Host (A) record.
Master Stack | The Master Stack is used by the following, therefore it helps users if it has a recognizable and convenient DNS Name such as tachyon - this is specified during installation of the 1E server using 1E Server Setup.
Platform services also reside on the Master Stack, which non-1E clients connect to, for example:
|
DMZ Server | The DMZ Server is a type of Response Stack used to provide 1E Real-time and Inventory services to Internet-based clients. It requires an external DNS Name - for example tachyonext - this is specified during installation of the DMZ Server using 1E Server Setup. The DNS Name is shared between the Switch network interfaces and Background Channel on the DMZ Server, and specified during installation of 1E platform clients, and stored in their configuration file. |
Response Stack | A Response Stack is used to provide 1E Real-time and Inventory services to clients on the internal (corporate) network. The choice of DNS Name is discussed in the table below. The DNS Name is shared between the Switch network interfaces and Background Channel on the Response Stack, and specified during installation of 1E platform clients, and stored in their configuration file. |
The number of DNS Names used by a system depend on the location of 1E and other Platform services. The table below describes options.
Single DNS Name | A 1E system can have a single DNS Name if all components are installed on the same server, for example tachyon - this is specified during installation of the 1E server using 1E Server Setup. If the server has multiple Switches, and therefore multiple network interfaces, then the same DNS Name can be shared by all Switches, the Background Channel and Master Stack. | ||||||||
Multiple client-facing DNS Names | The following client-facing components can each have their own DNS Name:
NoteMaster and Response Stacks must have different DNS Names if they exist on different servers:
When a Response Stack is installed on the same server as Master Stack, it will normally share the same DNS Name as Master Stack as described under Single DNS Name. However, if you have multiple Response Stacks and want them to share the same DNS Name, then the Master Stack must use a different DNS Name. This approach of all Response Stacks sharing the same DNS Name simplifies adding further Response Stacks at a later date. During installation - using 1E Server Setup - you need to consider the following:
If Master and Response Stacks are on the same server and you want them to have different DNS Names, then use the main binding for client connections to the Response Stack (because it is client-facing) and use the Alternate binding for other connections to the Master Stack. A simpler option is to put the Response Stack on its own server. Remote Response Stacks are recommended if the Master Stack is also hosting services AppClarity Software Reclaimer or Application Migration. If you want to configure Switches on the same server to use multiple DNS Names, you will need to seek guidance from 1E. In most cases this is not required or recommended. | ||||||||
Internal DNS Names | A DMZ Server is a special example of a Response Stack. The DMZ Server itself requires two DNS Names:
NoteBoth DNS Names must be included in the web server certificate. You can manually replace the external/client facing certificate after installation, to comply with best practice not to expose internal names in an external facing certificate. The internal Response Stack also requires an additional DNS Name - for example tachyonalt - for internal communications with the DMZ Server. Please refer to Implementing a 1E DMZ Server for more detail about DMZ Servers. |
Note
Note
1E Setup supports installation of one HTTP and up to two HTTPS bindings, but you can manually add more bindings after installation.
1E Setup currently supports only one Web server certificate, which must contain all the DNS Names used by the HTTPS bindings on that server. Each DNS Name must be included as a DNS Name in the Subject Alternate Name (SAN) entry of the web server certificate.
You can manually add more certificates, and change bindings. Please refer to Certificate requirements . Please note that 1E Setup helps maintain the main and alternate HTTPS bindings using one certificate.
Service Principal Names
1E platform and applications use underlying IIS and SQL Server technology, and only require HTTP or MSSQLSvc class SPNs if your company security policy has configured IIS or SQL Server to use Kerberos authentication.
If your IIS server is using Kerberos, then each DNS Name used to access a 1E Web Server requires an HTTP class Service Principal Name (SPN) to be registered against the relevant service account in Directory, which is computer$ by default. This allows 1E web applications to authenticate clients using Windows Authentication where Kerberos is an authentication provider (primary, fallback or negotiated).
Note
If your IIS server is using Kerberos then HTTP SPNs are required for web applications that use Windows Authentication, and are created using:
The web application pool's service account, which is Network Service for all 1E application pools, and therefore is the computer$ account
Each (A) Host record used to access the web application. If the server is accessed using a CNAME record, then you need to register an SPN for each (A) Host record used by the CNAME. A CNAME will have multiple (A) Host records when using round-robin or NLB to access the web server.
SPNs are not required for DNS Names used to connect to Switches or Background Channel, because they do not use Windows Authentication. However, bear in mind the same DNS Name might be used to access other web applications.
Downloading client content and Content Distribution integration
1E Client downloads content from the 1E Background Channel. Content is mainly scripts and other files required by instructions. It also includes client resources such as extensible modules, providers, and other dependencies to maintain the 1E Client. In most cases, client resources are version controlled to prevent repeated downloads. 1E instructions always request a download even if they have run an instruction before, unless the content for that instruction has been cached in memory.
You may need to consider the impact on the network if there is a large amount of content included in an instruction. This is more of an operational consideration instead of a design consideration.
Content Distribution is an optionally licensed component of the 1E Client. It makes software deployment, patching and downloading content more efficient and reduces the impact on the network. It removes the need for remote Distribution Point servers in Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager systems. When Content Distribution is installed on computers, it automatically elects a peer to download content from a server over the WAN and then peer-shares the content with other PCs at the same location. The downloaded content is cached locally on each PC in case it is needed again.
1E can optionally use Content Distribution to download content from servers irrespective of whether Content Distribution is integrated with Configuration Manager or not, and also uses advanced Content Distribution features.
1E client integration with Content Distribution disabled
If Content Distribution integration is not used, the following apply:
1E platform client waits a randomized stagger period defined by its DefaultStaggerRangeSeconds setting, and then downloads content from the specified Background Channel.
1E platform client retains modules and extensibles that it has downloaded, but does not retain instruction scripts after they have been run. Any instruction that requires a script or other file will download the latest version each time the instruction is run.
1E Client integration with Content Distributionenabled
Content Distribution integration is available on Windows PC devices and is enabled by default, but can be disabled during installation of the 1E Client.
With the Content Distribution integration feature enabled, 1E Client will detect if a supported version of Content Distribution is running on the device.
1E Client immediately requests Content Distribution to download content from the specified HTTP source, such as the Background Channel. Content Distribution behaves in the same way as it does with Configuration Manager by ensuring the latest version of content is obtained and electing a master to perform the actual download.
Content Distribution maintains its own cache of downloaded content which avoids the need for repeat downloads over the WAN, and provides content to peers that require the same resources which avoids peer devices having to download over the WAN.
If the Content Distribution integration feature is enabled, and requested content is not provided within the timeout period, the 1E Client will fall back to downloading directly from the HTTP source. The most likely reason for a timeout is if Content Distribution is busy downloading other content.
To use Content Distribution, there is no special configuration of 1E Servers unless you want to use server-based features provided by the Content Distribution and Content Distribution, which requires the reverse proxy feature to be configured on Background Channels.
The Background Channel is a web application on the 1E Server which uses HTTPS and default port is 443. The URL for the Background Channel is defined in the 1E Client configuration file and is specified during installation of the 1E Client if 1E features are enabled. The 1E Client passes this URL to Content Distribution when it requests content to be downloaded. Instructions can also specify other HTTP sources.
Content Distribution does not need to be configured to use certificates in order to communicate with the Background Channel (the Content Distribution CertIssuer and CertSubject settings are used only with Configuration Manager Distribution Points that are configured to validate device certificates).
The Nomad Single-Site Download (SSD) feature, which uses Content Distribution, further reduces the impact of downloading content over the WAN.