Nomad overview
An overview of features and enhancements.
Nomad removes the need for distributed servers and intelligently uses only available bandwidth for all content distribution, so the business is never impacted by Configuration Manager or Windows deployments.
In the world of Windows 10 and modern management, there is more content being distributed on your network than ever before to get Windows and applications deployed and keep them up to date. While you are carefully managing some of those deployments through Microsoft Endpoint Manager, others are out of your control. Modern applications self-update, Windows updates may be pulled as required based on policies and users have access to download apps from the Microsoft Store or Store for Business. A lot of that activity is currently invisible to you and may be causing you to miss compliance deadlines.
There is no single, comprehensive view of exactly what is being distributed, to where and from which sources, so you don’t really have a clue how it is all affecting your network. How well are peer-to-peer technologies (Nomad, Delivery Optimization) working to reduce the effect this content distribution has on your WAN bandwidth usage? How can you make them more effective? These are the questions we can answer with the Nomad.
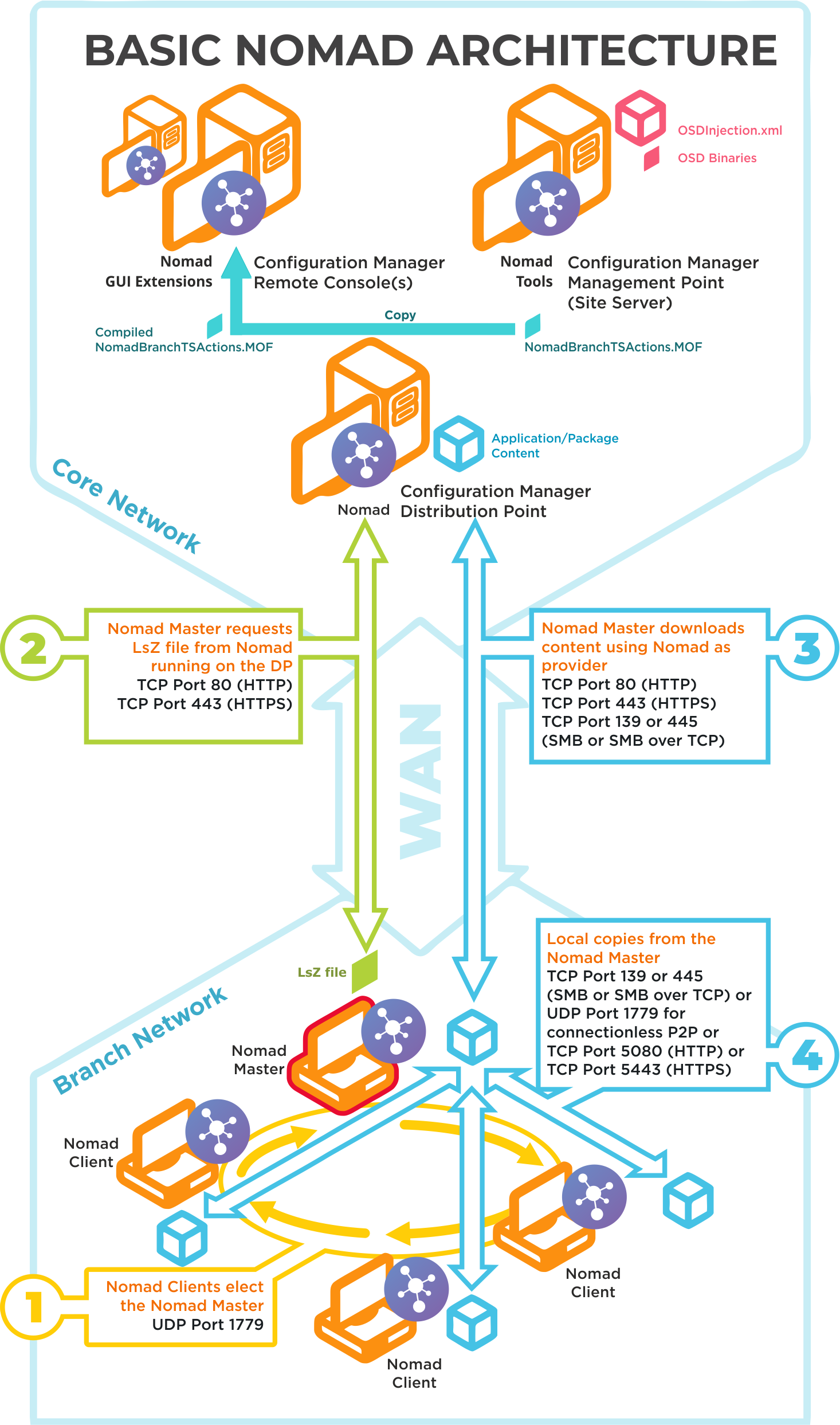
Simple Nomad Architecture
In response to customer demand to simplify the deployment, we’ve made two architectural changes:
Reduced the number of agents required - 1E has merged the client functionality of Nomad, PXE Everywhere, WakeUp, Shopping and Tachyon into a single 1E Client.
Modernized the back-end infrastructure - Nomad requires a back-end server, which was previously our legacy ActiveEfficiency platform. This now is replaced with the unified Tachyon Platform.
The 1E single agent and platform is a remote endpoint management solution designed to significantly improve IT’s ability to support the Work From Anywhere Enterprise. Built around a revolutionary real-time engine, and providing both holistic digital experience monitoring and remediation, it’s a powerful tool that helps IT to deliver great employee experiences, anywhere.
Once you are on the Tachyon Platform, you can enable further features including Experience, User Sentiment, Guaranteed State and Patch Success, as well as opening up real-time management to any task by acquiring the appropriate license. To find out more, refer to Introducing Tachyon.
Ports | Notes |
|---|---|
UDP 1779 | Step 1By default, Nomad uses UDP Port 1779 to communicate during the election process for determining the master on a subnet. The Nomad installer will automatically add The default value for the port may be changed at install time using the MODULE.NOMAD.P2PPORT installer property or post-installation by changing the P2P_Port registry value. If you change the default port, you must ensure all Nomad clients communicate using the same port. The Nomad port (by default UPD Port 1779) must be open on all wireless access points to facilitate Nomad peer-to-peer communications. Not all vendors enable this port by default, please refer to the specific device vendor's documentation for details on how to enable ports on each WAP device. |
TCP 80 (HTTP) TCP 443 (HTTPS) | Step 2Nomad Master requests LSZ file from Nomad running on the DP. |
TCP 80 (HTTP) TCP 443 (HTTPS) TCP 139 (SMB) TCP 445 (SMB over TCP) | Step 3Nomad Master downloads content using Nomad as provider. This communication depends on how the DP is configured. It may be one of the following:
For Configuration Manager the default setting is HTTP or HTTPS. |
TCP 139 (SMB) TCP 445 (SMB over TCP) UDP 1779 (used for connectionless P2P) TCP 5080 (HTTP) TCP 5443 (HTTPS) | Step 4Local copies from the Nomad master. The recommended way to facilitate Nomad cache access is to enable Windows File and Print Sharing. If this is not feasible on your network environment you can configure Nomad to use different means to access network shares, see Nomad cache for more details on configuring this option. Connections may use one of the following:
|
Nomad Security
Nomad is a peer-to-peer technology that works by using HTTP/HTTPS or the native Windows OS File and Print Sharing services to share content among computers.
With Nomad, you get improved security features like:
Certificate-based client authentication for peer-to-peer communication, removing the need for a local user account.
Support for Enhanced HTTP in Configuration Manager, including support for removal of the CM Network Access Account support for multiple Certificate Authorities when using HTTPS for peer-to-peer communication.
For more details about Nomad security refer to Ensuring Nomad is secure.